Glanceable AR Launcher
AR headsets have the potential to be an effective medium to display various information needed by users. In this project, I explored the paradigm of glancability for AR headsets by implementing a glanceable AR “launcher” which uses the user environment to be unobtrusive while still being effective at providing information to the user. The proof of concept is implemented using Three.js, and can be viewed below.
Glanceability
The primary aim of the launcher is to display information from subscribed feeds to the user. The user interface needs to provide feed and region management commands, and can be minimal. The necessary UI functions needed are:
- Subscribing and unsubscribing to a new feed
- Enabling/Disabling feeds
- Grouping feeds together
- Pinning a region to a surface
Glanceable is said to be the quality of letting users get information quickly and with low effort. Glanceable visuals are fastest interacted with when they have a high degree of symbolism, or are text. To that end, all feeds described in this interface have a primary and secondary context. The primary context provides a visual to distinguish between feeds when quickly navigating to a particular feed. The secondary context is shown when the user is looking at a feed, and adds more detail to the feed and the user interface. An example of both can be seen below.
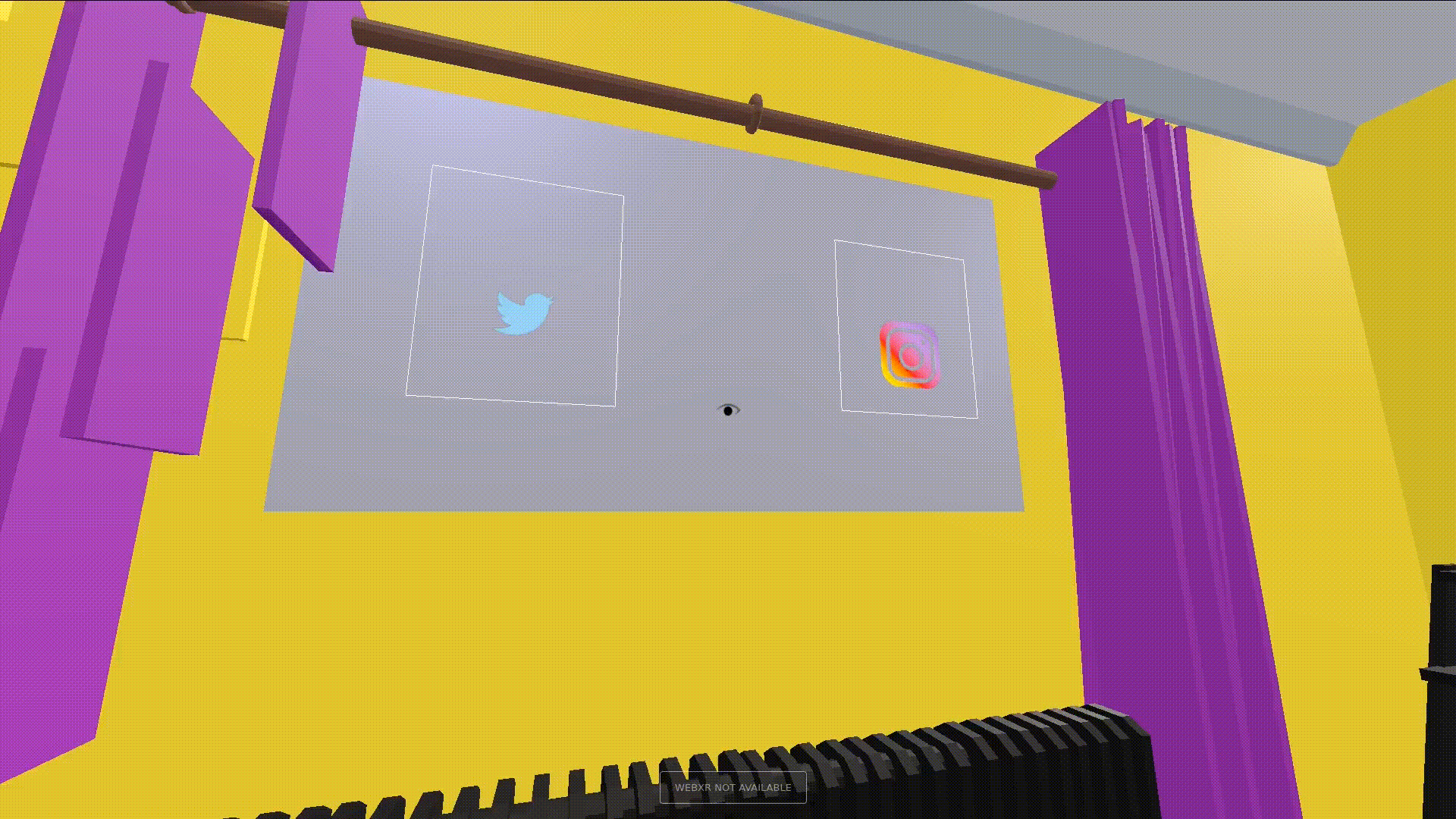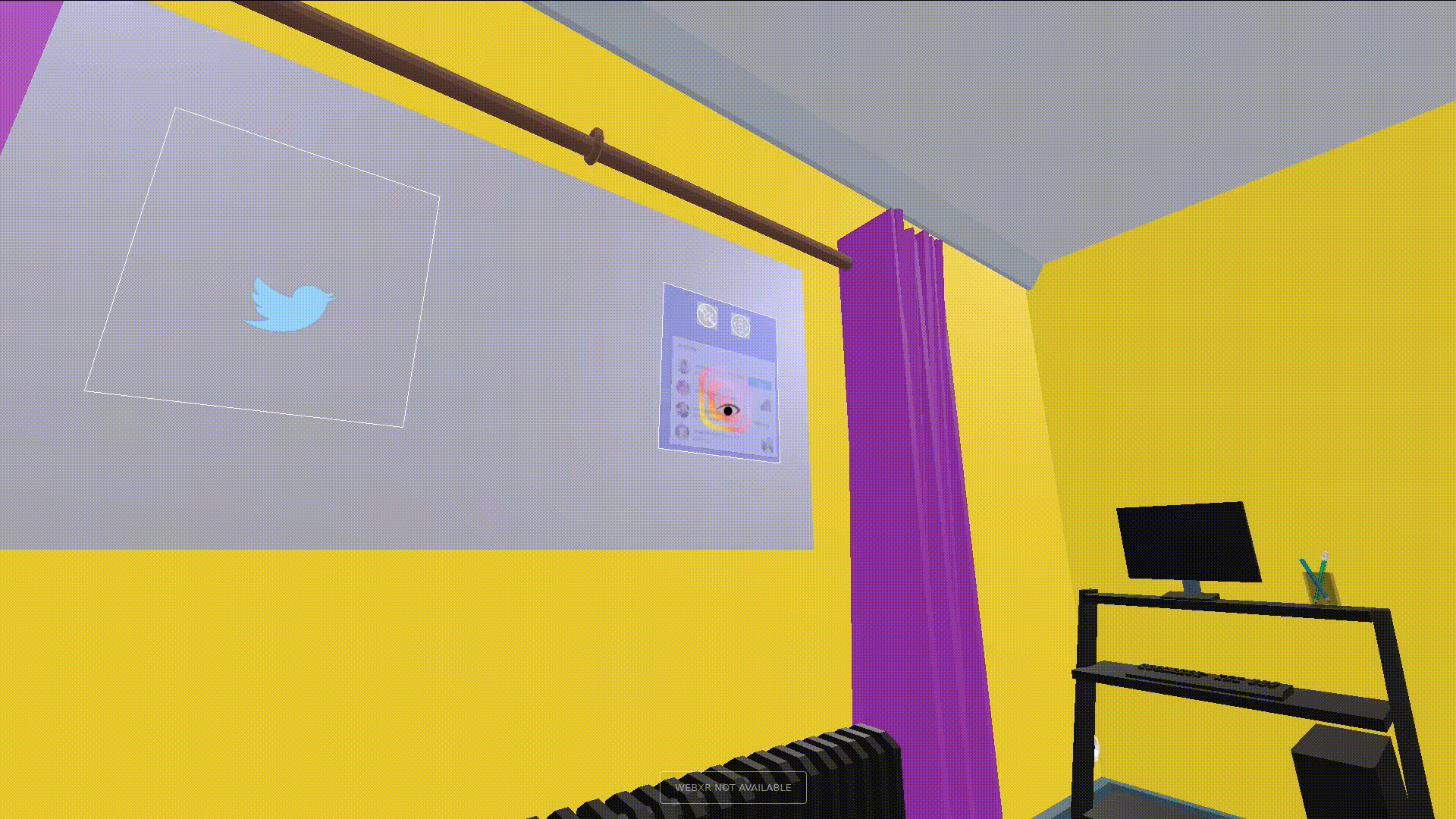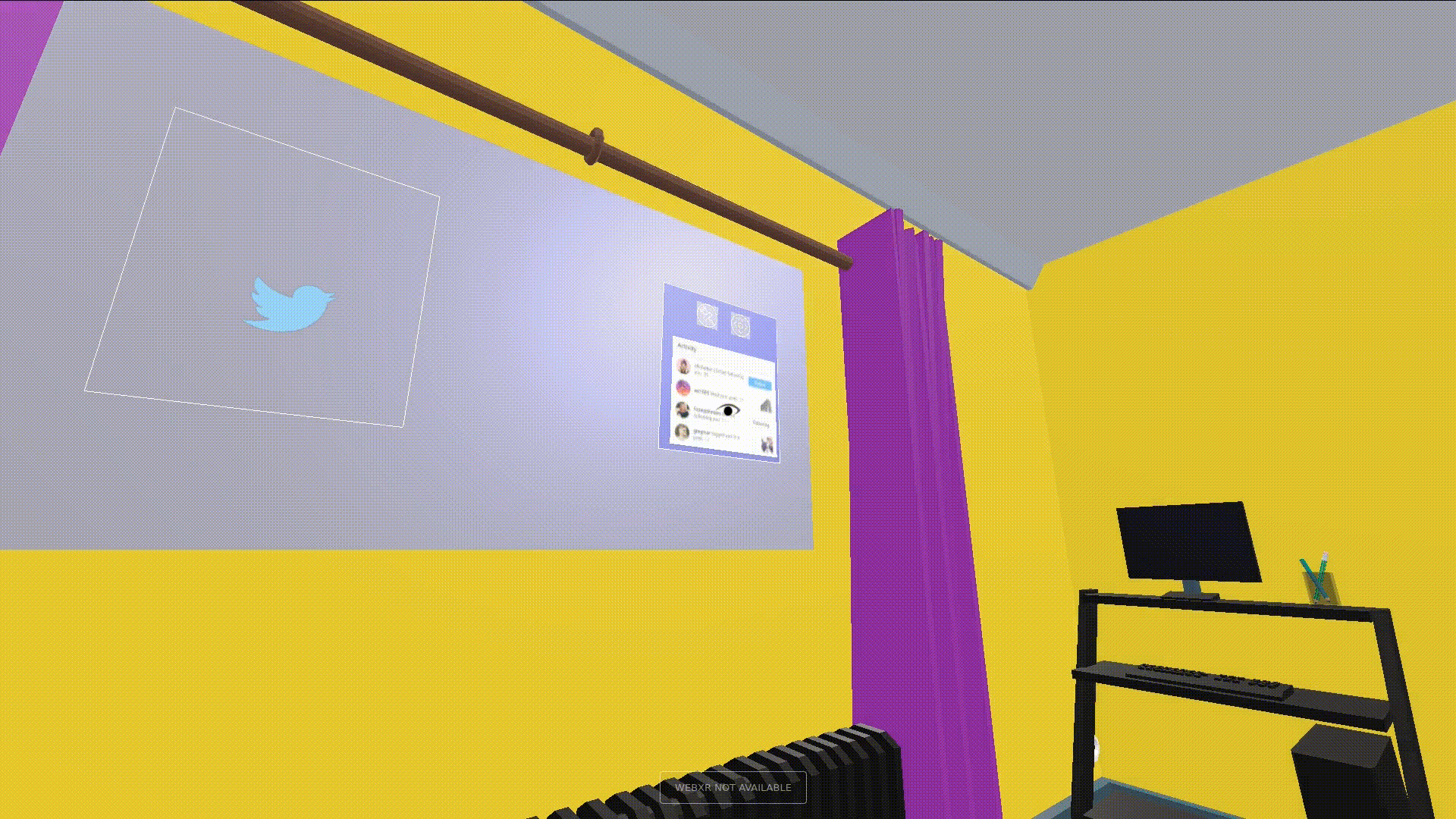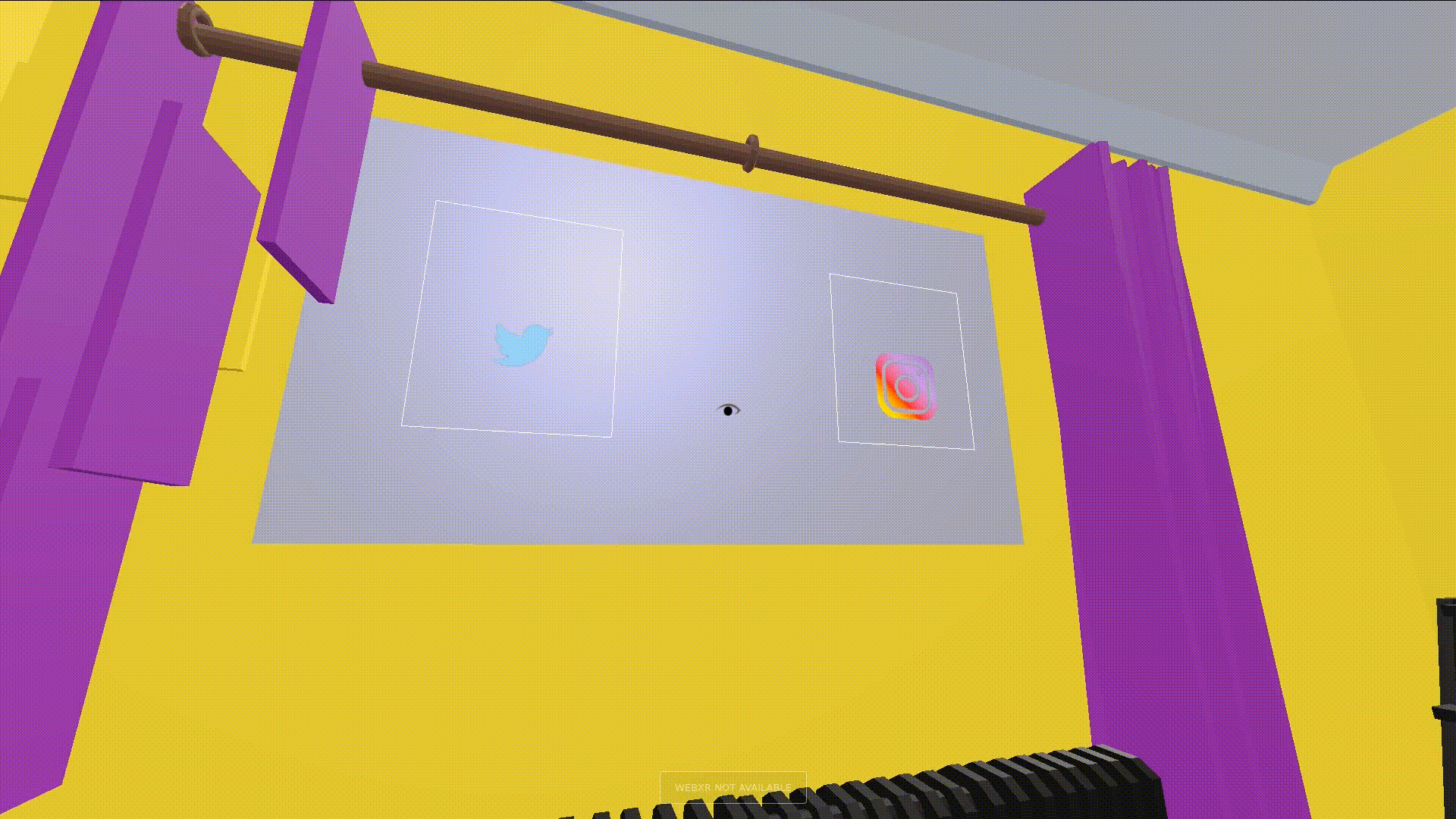
Apart from the contexts, we make sure that the UI is highly responsive to where the user glances to it. Every element gives feedback for a glance to the user. We define a “Glance Attention Area”(GAA) as the relevant focus area around the tracked eye of the user. GAAs are typically circular to denote the area the eyes are looking at, but can be different geometries depending on the application. To make the interface appealing, the primary context is switched to the secondary whenever the context intersects with the user’s GAA. The actual area of the GAA depends on the application and how detailed its interface needs to be. In our case, the GAA is wide when the user is looking at primary contexts to focus on, and narrows down when the user is interacting with the secondary context, e.g. to click on an icon.
Interaction examples
The implemented UI interface functions are:
- Enabling/Disabling feeds

- Grouping feeds together

- Pinning a region to a surface

Demo
Created using THREE.JS, I hope that this demo can showcase the interface experiments I am performing with glancable AR, real world spaces and WebXR. Note: In VR Mode, the controllers might not function properly and crash the demo. I am working on that issue, estimated update: 15/06/2020


